Articles Nerves
The brain sends and receives information to the body through the nerves. This is similar to a cable that connects a computer to a printer. Nerves have different jobs and control both voluntary (i.e. walking) and involuntary actions (i.e. sweating, digestion). Injuries to the musculoskeletal skeletal system can result in damage to the nerve tissue and give rise to specific signs and symptoms.
Symptoms (what you feel):
- pain
- burning
- tingling
- pins and needles
- numbness
- electric shocks
- hypersensitivity to pain
- weakness
Signs (what a clinician sees):
- specific muscle weakness
- muscle wasting
- loss of balance or coordination
- paralysis
- loss of pelvic floor control
- impaired movement
- abnormal sweating, skin texture and colour changes of the affected area
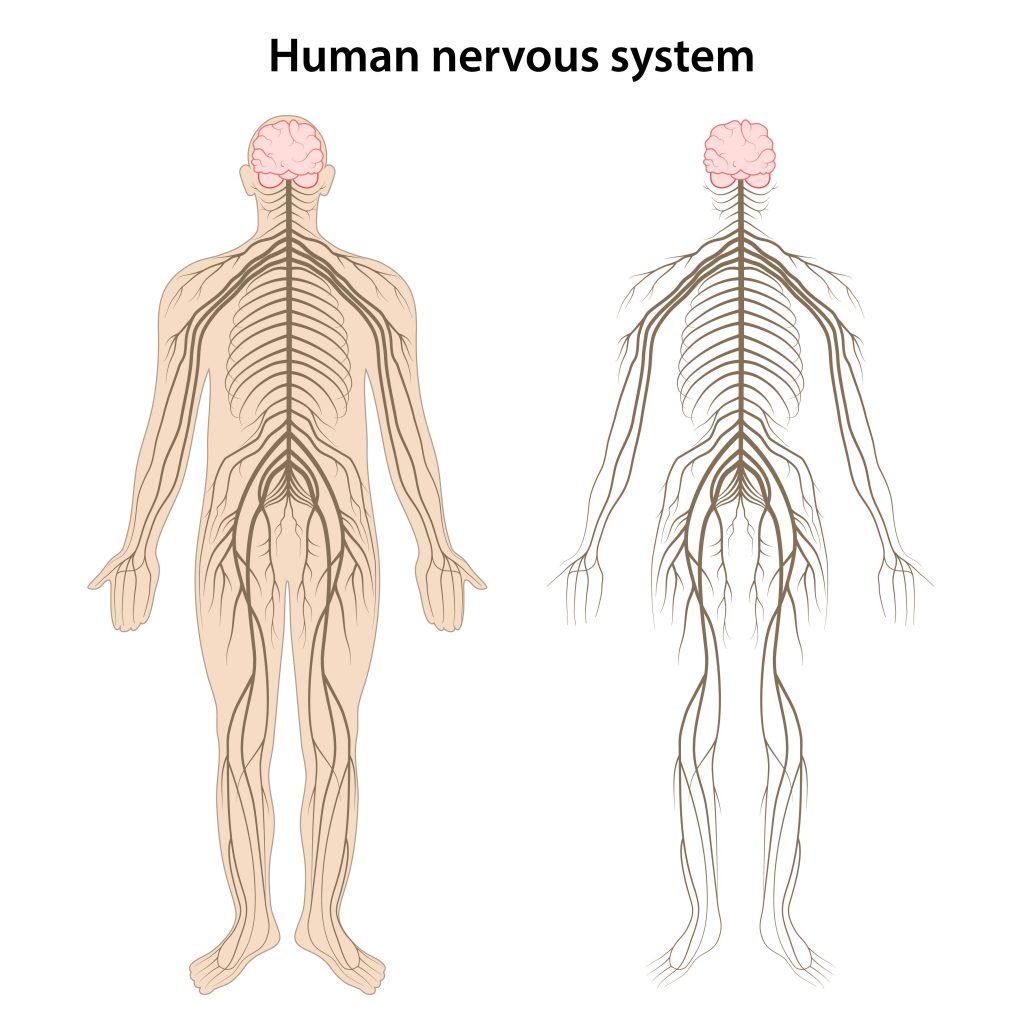
Common causes of nerve injuries include:
Inflammation
Following an acute injury, inflammatory chemicals can irritate the nerve endings. Prolonged inflammation can lead to ongoing signs and symptoms of neural irritation.
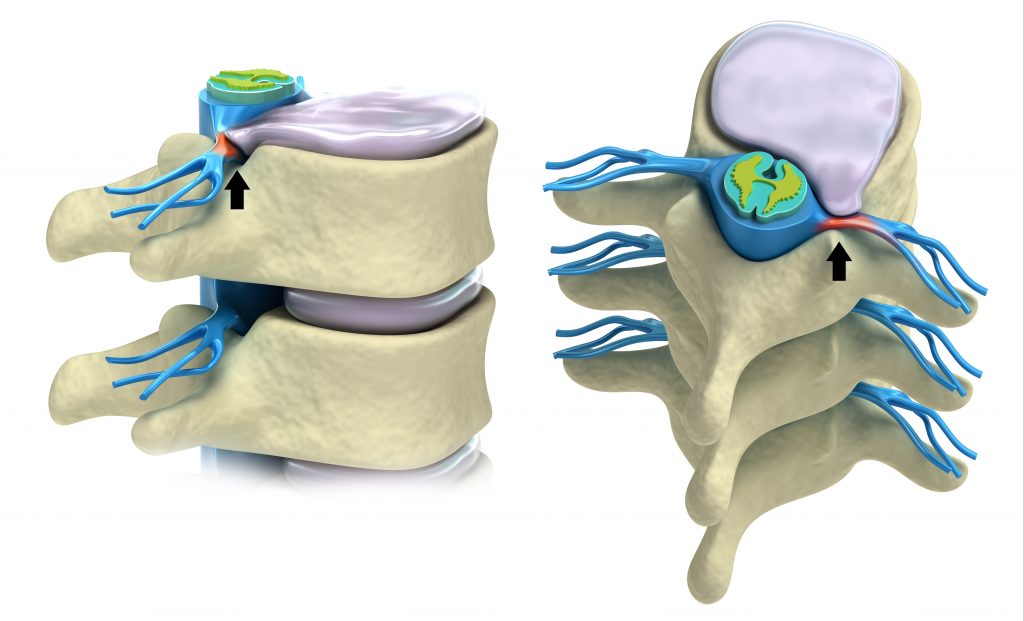
Nerve Compressions
These are also known as “pinched” or “impinged nerves”. Unfortunately the human body has some design flaws, where the nerves can be compressed by surrounding anatomical structures as they navigate their way through the body. This is commonly seen in the spine (disc bulges), wrists (carpal tunnel syndrome), and elbows (cubital tunnel).
Crush Injuries
As the name suggests nerves can be injured as a result of being crushed, these are usually seen in occupational and motor vehicle accidents.

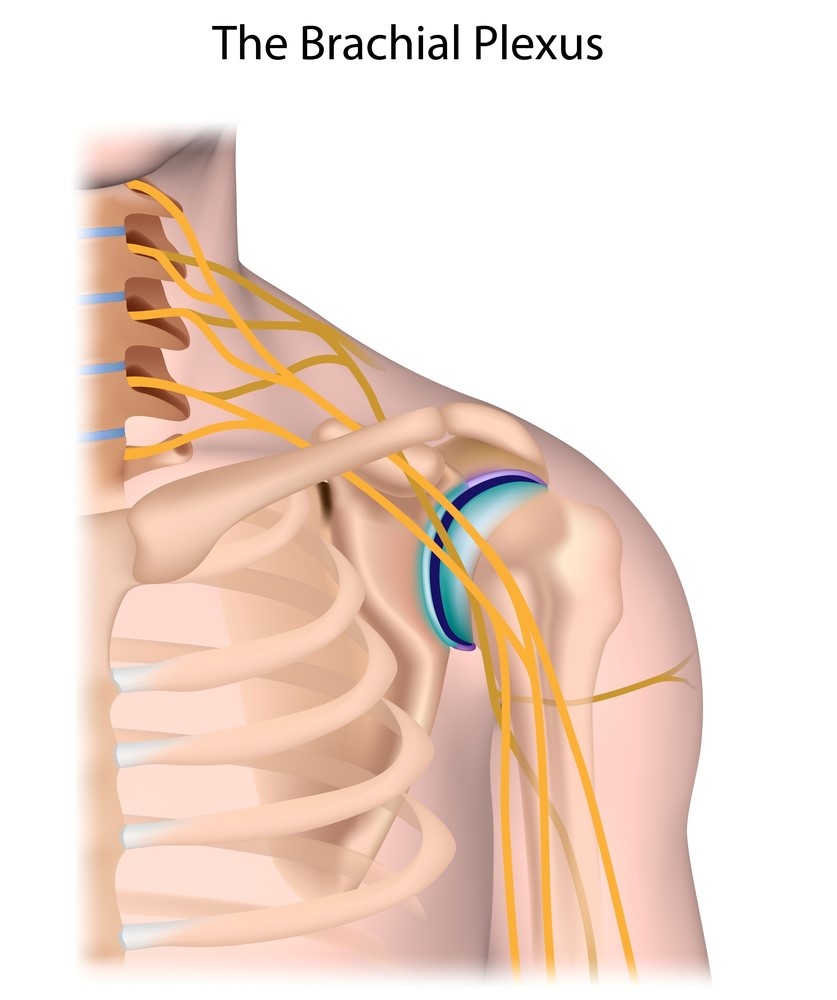
Traction Injuries
These injuries arise from suddenly overstretching the nerve tissue. A common site of injury is the brachial plexus, a network of nerves arising from the neck and shoulder. This typically occurs when the arm is violently pulled downwards or following a very hard shoulder charge. In extreme circumstances the nerve can actually be completely torn off the spinal cord!
Lacerations
Nerve lacerations are often seen in the hands and can require surgical repair. Ongoing symptoms such as numbness, sensation changes and pain commonly persist after these injuries.

Central Sensitisation
Central sensitisation is a complication that develops after an acute injury. The body becomes more sensitive to painful and non-painful (i.e. light pressure) sensations due to changes in how the brain processes this information. This condition explains why some people continue to experience pain for several years after an injury.

Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
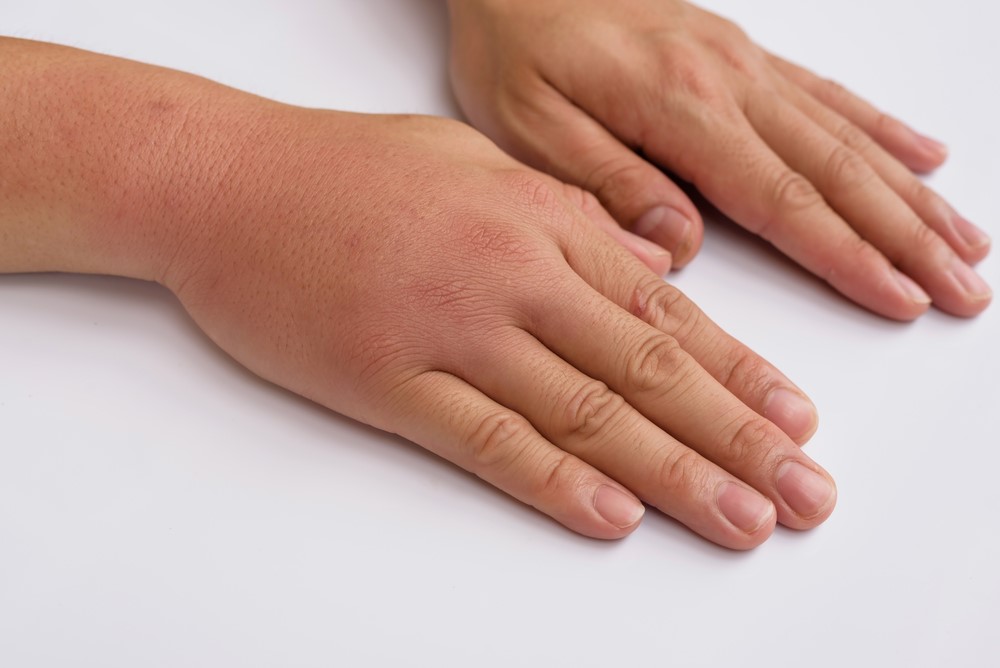
CRPS is a chronic pain condition that develops after trauma to the musculoskeletal system (i.e. fracture, surgery) making the nerves overactive and hypersensitive . Apart from being painful, the injured area can show signs of:
- chronic swelling
- abnormal sweating
- abnormal changes in skin temperature
- abnormal changes in skin colour (red and blue)
- restricted movement
- changes in nail and hair growth
Please keep in mind the information provided is general in nature and should not be used as a substitute to consult your treating health professional. If you have any specific questions or require assistance with your individual treatment requirements please do not hesitate to contact MyFamily Physio Mona Vale, Northern Beaches Sydney.
Related Articles